How Does Ultrasound Work
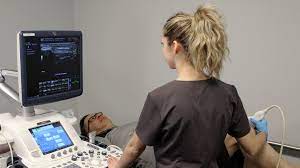
Ultrasound is a type of sound waves with frequencies higher than how does ultrasound work the human ear can hear. It’s used in many medical applications, such as prenatal care, to get a clear picture of the developing baby. How does ultrasound work? Sound waves are produced when electricity is passed through a piezoelectric crystal. The frequency of the sound waves produced can be changed by altering the voltage applied to the crystal. When the sound waves bounce off structures inside the body, they create echoes. These echoes are picked up by the transducer and converted into electrical signals, which are then displayed on a screen.
Ultrasound is an important tool in modern medicine. It has a wide range of applications, from helping doctors get a clear picture of a developing baby to diagnosing abdominal pain. But how does ultrasound work?
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a type of sound waves with frequencies higher than those that humans can detect with their ears. It has many uses, including in medical imaging, industrial inspection, and communication. In medicine, ultrasound is used to create images of internal organs or to guide procedures such as needle biopsies. It is also used in pregnancy to listen to the baby’s heartbeat and check for birth defects. Industrial applications include detecting flaws in materials and measuring the thickness of objects. Ultrasound can also be used for cleaning and for breaking up kidney stones.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound waves are created when sound waves vibrate at a frequency above 20,000 Hz. When these waves bounce off of an object, they create echoes. These echoes can be detected by special sensors called transducers. The information from the echoes is then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
What are the different types of ultrasound?
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from “normal” (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in young adults.
There are two main types of ultrasound: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic ultrasound is used to image the body for diagnostic purposes. Therapeutic ultrasound is used to treat various conditions such as pain relief and tissue healing.
Diagnostic ultrasound imaging is typically performed using a transducer (probe) that emits and detects ultrasonic waves. The waves are transmitted through the body and reflect off of internal structures. The reflected waves are detected by the transducer and converted into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by a computer to create an image.
Therapeutic ultrasound uses a different type of transducer that generates heat when exposed to ultrasonic waves. This heat can be used to treat conditions such as pain relief and tissue healing.
Diagnostic ultrasound imaging is performed using a transducer that emits and detects ultrasonic waves. The waves reflect off tissues in the body and are detected by the transducer. The reflected waves are converted into electrical signals that are displayed on a monitor as images.
Therapeutic ultrasound uses a similar process, but the transducer delivers ultrasonic energy to the body instead of just detecting it. This energy can be used to heat tissue or break up kidney stones, for example.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound is an imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal body structures. The images produced can be used to detect and diagnose various medical conditions.
How does ultrasound work?
The basic principle behind ultrasound is relatively simple. When sound waves of a high enough frequency are directed at the body, they reflect off of internal structures and create echoes. These echoes are then detected by a special transducer and converted into electrical signals. These signals are then displayed on a screen, allowing the physician to visualize the internal structures of the body.
What are the different types of ultrasound?
There are two main types of ultrasound: diagnostic and therapeutic. Diagnostic ultrasound is used to image the body for diagnostic purposes. Therapeutic ultrasound is used to treat various conditions such as pain relief and tissue healing.
How does ultrasound work?
Ultrasound waves are produced when sound waves vibrate at a frequency above 20,000 Hz. When these waves bounce off an object, they create echoes. These echoes can be detected by special sensors called transducers. The information from the echoes is then converted into images that can be viewed on a monitor.
Ultrasound can be used to image many different parts of the body, including the heart, blood vessels, kidneys, liver, and even unborn babies. It is a non-invasive technique that carries very little risk to the patient.
What are the benefits of ultrasound?
Ultrasound waves have many benefits and uses in the medical field. They can be used to create images of the inside of the body, which can help doctors diagnose problems and plan treatments. Ultrasound waves can also be used to break up kidney stones, relieve pain, and speed up the healing process.
Are there any risks associated with ultrasound?
Yes, there are some risks associated with ultrasound. These include:
• heating of body tissues from the high-frequency sound waves
• possible damage to the eyes from direct exposure to the ultrasound beam
• burns from prolonged exposure to ultrasound gel
• potential for small air bubbles (“microbubbles”) to form in blood vessels and travel to the brain, which could cause a stroke.
Conclusion
Ultrasound waves are sound waves with a frequency above the human hearing range. When these waves hit an object, they cause it to vibrate. This vibration is then converted into electrical signals that can be processed by a computer to create an image. Ultrasound imaging is safe and painless, and it does not use ionizing radiation.







